Mysql deployment

MySQL: The Trusty Librarian of Data
MySQL serves as an open-source Relational Database Management System (RDBMS), offering structured data organization with SQL queries. It acts like a trusted librarian, ensuring data integrity, scalability, and ease of retrieval. MySQL's role extends from creating databases and defining tables to inserting, retrieving, and manipulating data, making it a reliable partner for various web and software projects.
Exposed Ports
| Port Type | Port Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Tcp | 3306 | MySQL exposes port 3306 for TCP traffic. |
| http | - | - |
Volume Mounts
MySQL uses volume mounts to manage data storage and configuration. You can set these when running the container:
| Volume | Description |
|---|---|
/my/custom:/etc/mysql/conf.d | Path to MySQL custom configuration files (conf.d). |
Environment Variables
MySQL requires environment variables to be set for configuration:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD | Password for the root user. (e.g., example) |
Installation
| Description | Decription |
|---|---|
| Docker Image | mysql👈(click me,for the dockerhub image) |
| Application name | Eg: mysql1(you can put any name) |
| Resource Allocation | 0-100%(10 % of your allocated resources (CPU, RAM) will be used for this application.) |
Protocol | |
| Http: | |
| Tcp: | 3306 |
| Advanced | Install with Default |
Steps And Procedure
For Detailed steps and procedure please vist this page: Click here
By following these steps, you can effortlessly deploy an MYSQL instance with your chosen configurations. This enables you to tailor the environment to match your application's requirements and specifications. Whether opting for the default installation or delving into advanced settings, our platform ensures a seamless deployment experience while providing you the flexibility to customize according to your needs.
Connecting to MySQL Database via MySQL Client
When deploying a MySQL application, you can't directly connect to it via a web browser as you would with HTTP applications. Instead, you need to use a MySQL client to establish a connection using the application's IP address, username, and password. Here's how to do it:
- Install MySQL Client: If you don't have MySQL client installed, you can download and install it on your local machine from the official MySQL website.
- Gather Connection Details: After deploying your MySQL application, note down its IP address, username, and password. You might have received these details during the deployment process or through an email.
- Open MySQL Client: Open your MySQL client application on your local machine.
- Create a New Connection: Look for an option to create a new connection or establish a new session. This might vary based on the MySQL client you are using.
- Enter Connection Details: In the connection setup, provide the following details:
- Host: The IP address of your deployed MySQL application.
- Username: The MySQL username associated with your application.
- Password: The corresponding password for the provided username.
- Connect: Once you've entered the details, click on the "Connect" or "Log In" button to establish a connection.
- Execute Queries: After successfully connecting, you'll be able to execute SQL queries, manage databases, and perform various database-related operations using the MySQL client interface.
Visual Snapshot
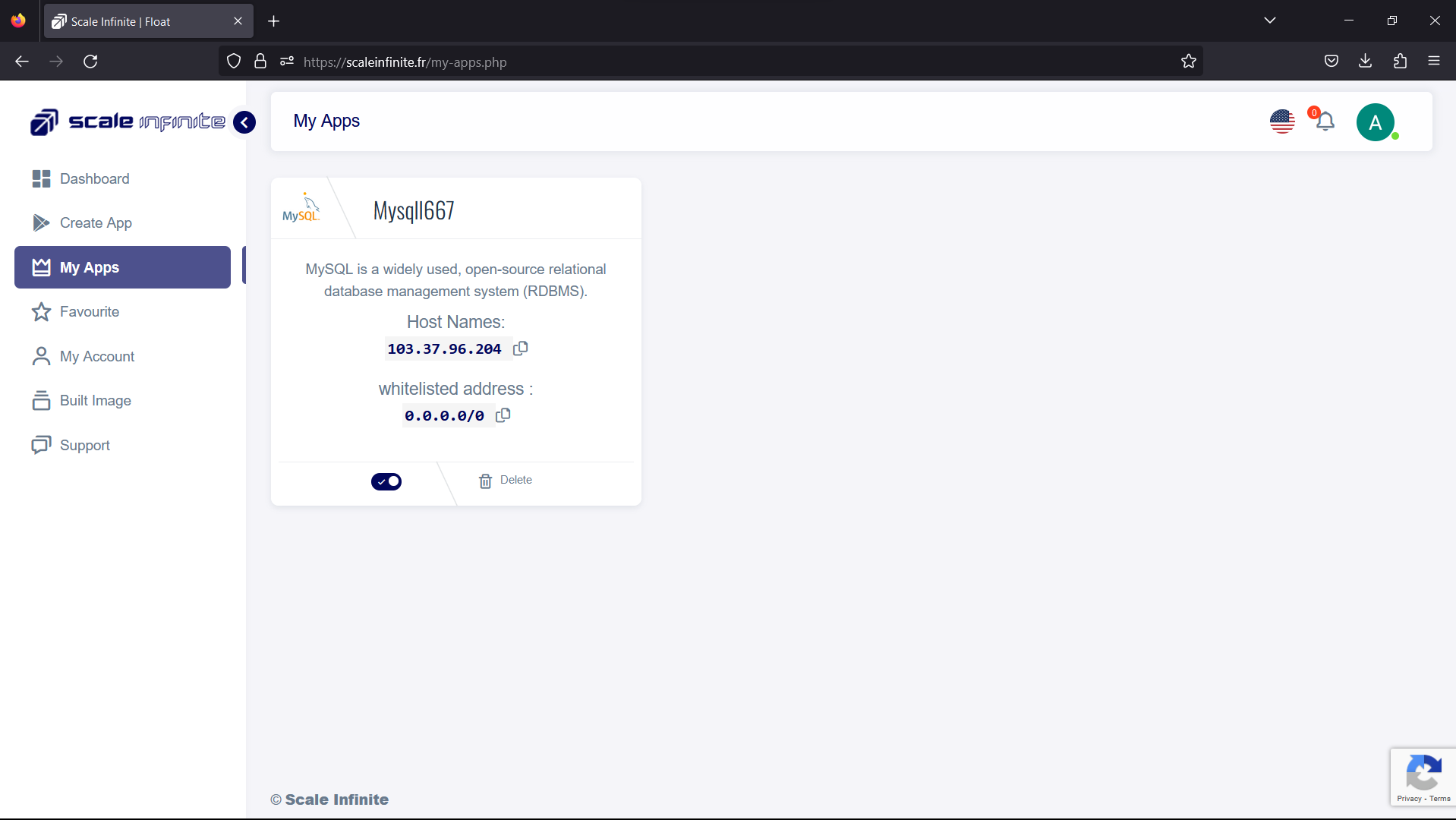
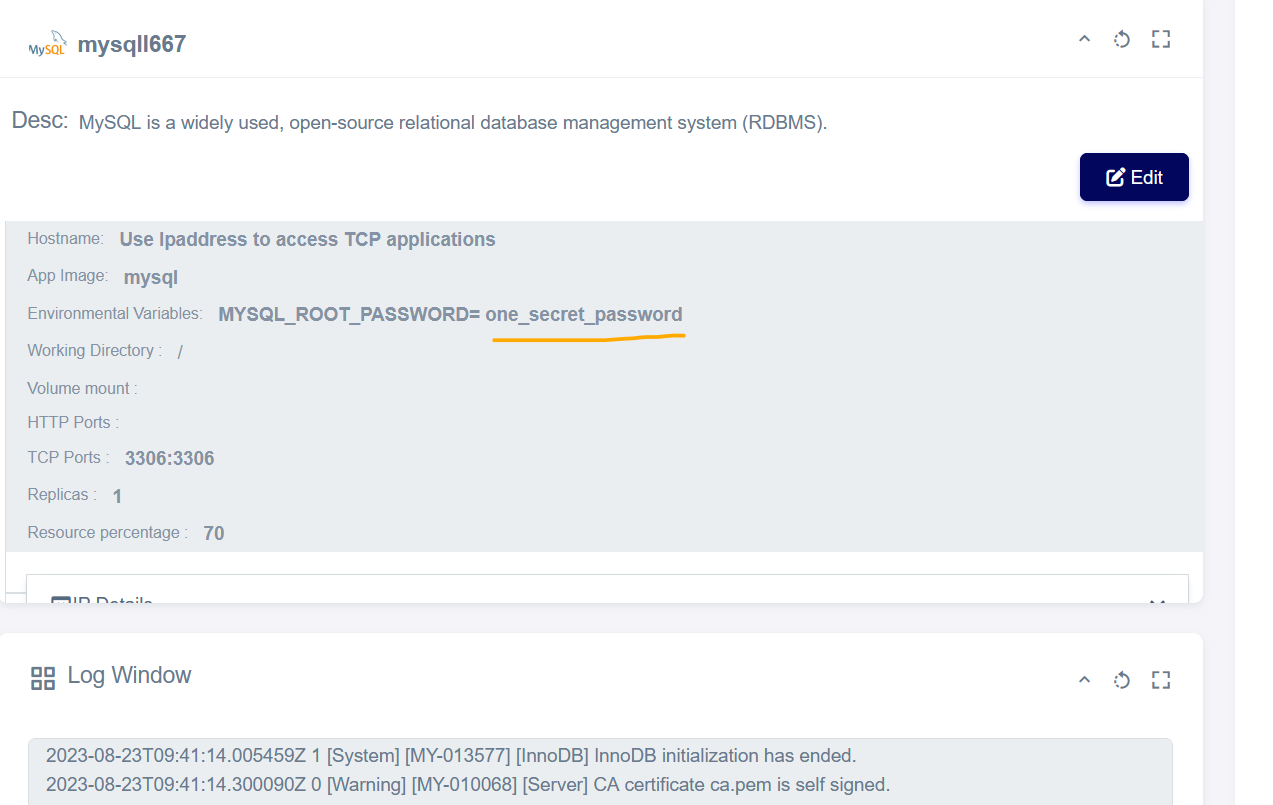
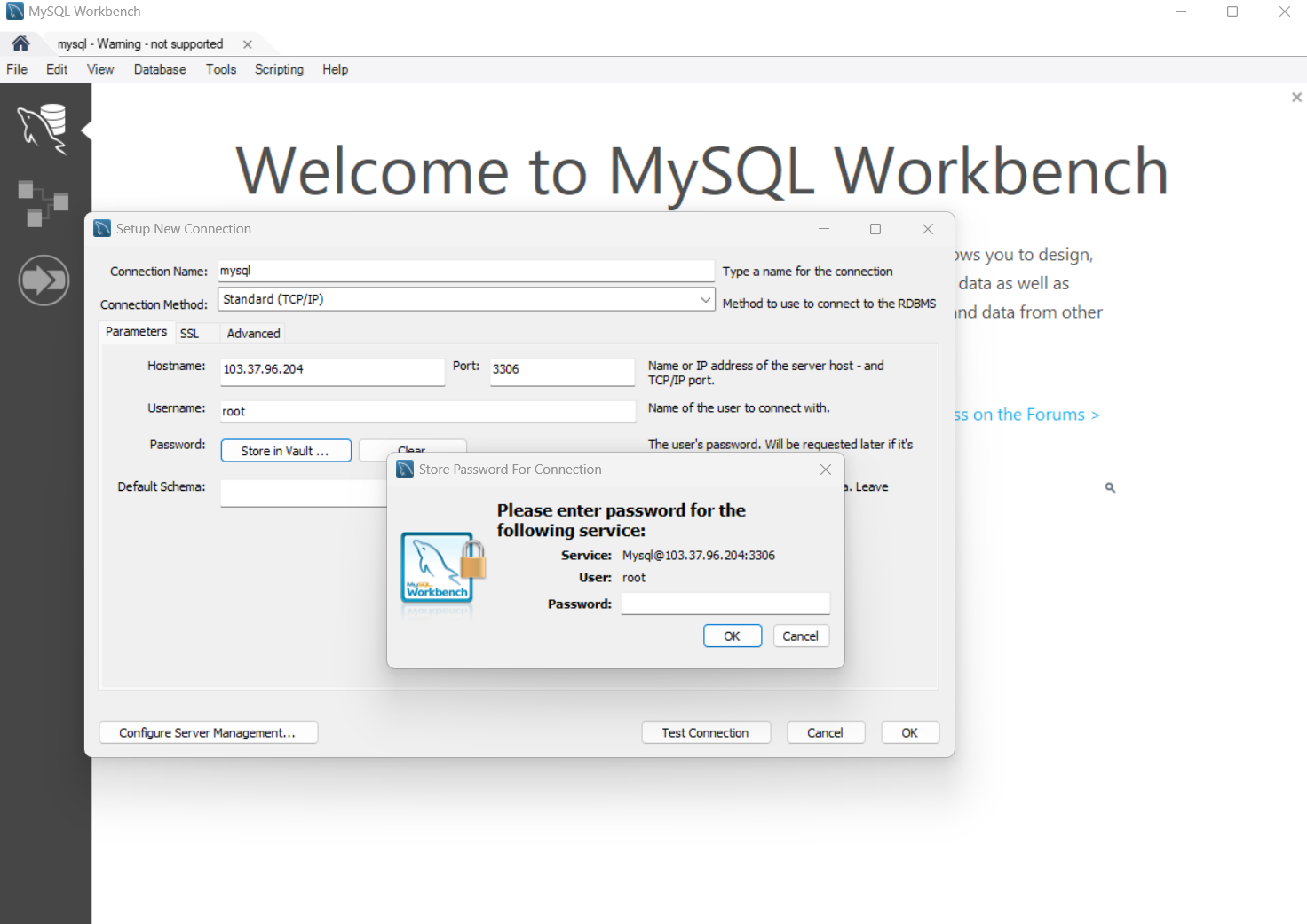
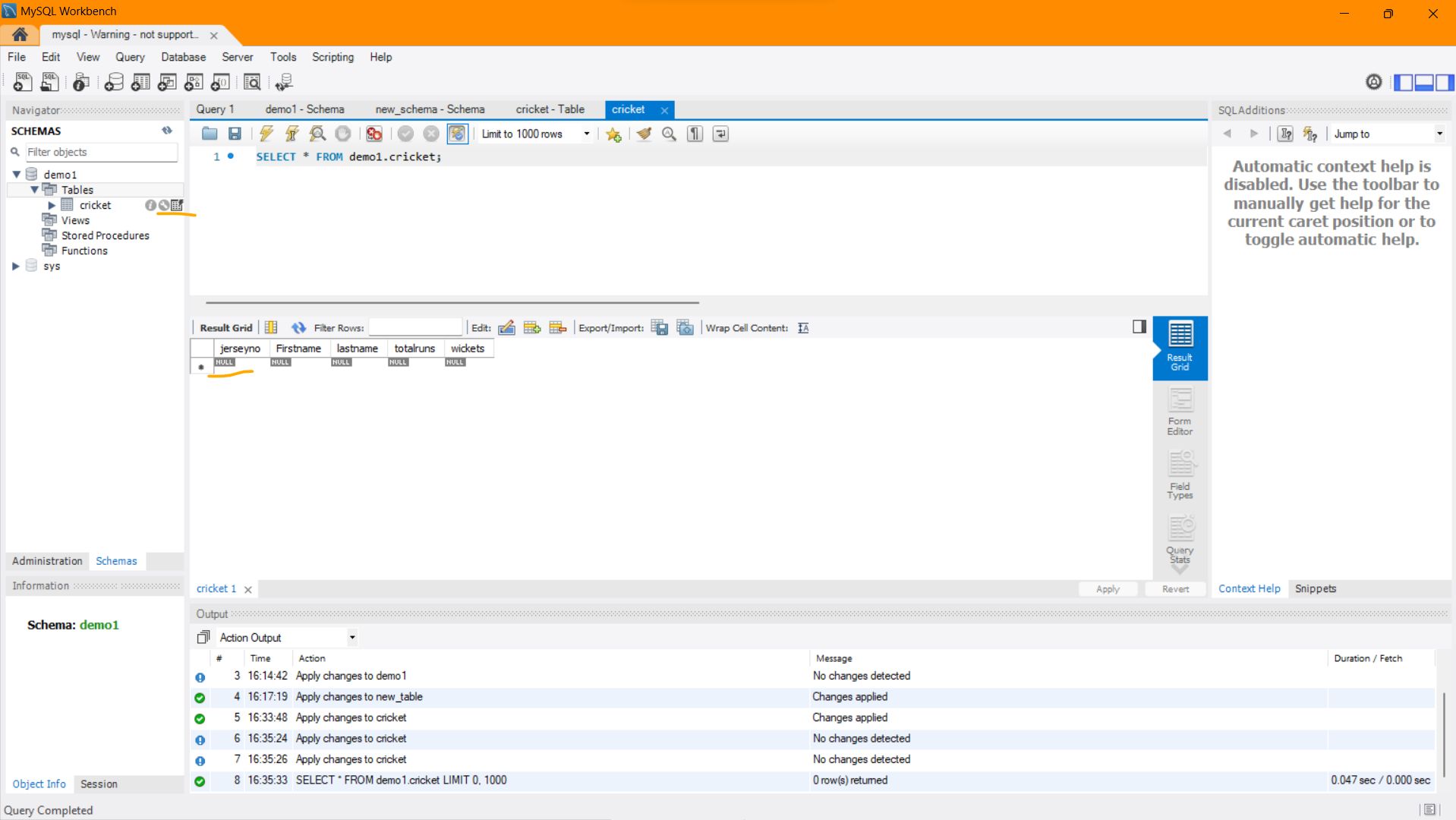
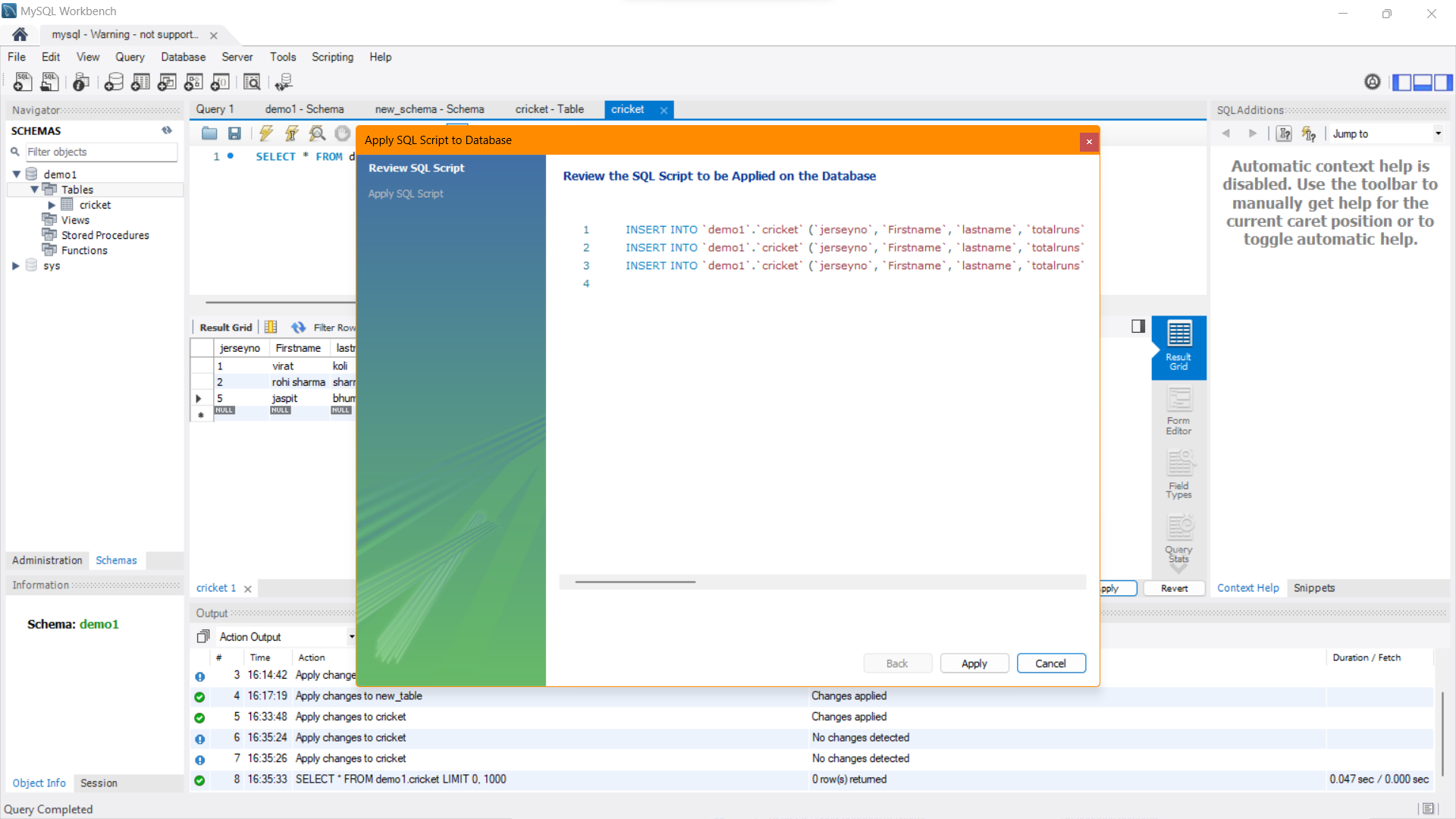
Youtube Tutorial
Check out our youtube video for more clarification.
FAQ
For Detailed FAQ please vist this page: FAQ
Join us
Stay informed and engaged with our project's latest developments and support on Slack. Join us today to connect, collaborate, and keep the momentum going!
Category
Kubernetes, cloud computing, DevOps, cloud services, hosting platform, container orchestration, cloud infrastructure, cloud deployment, cloud management, cloud technology, cloud solutions, database, mysql